DECARBONISING THE SECTOR
The ESA and its members are leading efforts by the recycling and waste treatment sector to reach net-zero emissions by 2040.
Log in for exclusive member content and access to our full archive.
- Home
- »
- The ESA’s work
- »
- Setting Standards
The recycling and waste treatment industry has reduced carbon emissions more than almost every other sector since 1990.
Furthermore, through our core recycling and waste treatment activities, our sector helps avoid millions of tonnes of CO2e emissions associated with society’s waste, across the wider economy, every year.
But our operations do still have a direct emissions impact and account for nearly eight per cent of total UK emissions.
To ensure we maximise our sector’s positive contribution towards the UK’s net-zero goals, the ESA and its members produced the first sectoral Net Zero Strategy in 2021, which sets out a credible plan and commitment to achieve net-zero emissions as a sector by 2040 – a full decade ahead of Government targets.
We will do this by decarbonising our vehicle fleets, increasing plastics recycling, moving organic waste out of landfill, improving the energy-efficiency of facilities and by developing carbon capture, usage and storage (CCUS) opportunities alongside greater use of district heating networks for energy-from-waste facilities.
Our members commit to reporting on, and monitoring, emissions progress and the ESA will continue to lead engagement with policy-makers to ensure the policy agenda supports delivery of our net-zero strategy. In particular, this includes promoting policy solutions for challenges outside of the sector’s full control – including support for plastics recycling, grid and transport decarbonisation and ensuring successful application of the Emission Trading Scheme (ETS) to the sector.
You can view and download the ESA’s Net-Zero strategy document and a selection of our latest decarbonisation news, analysis and publications below.
Generating energy from society’s rubbish
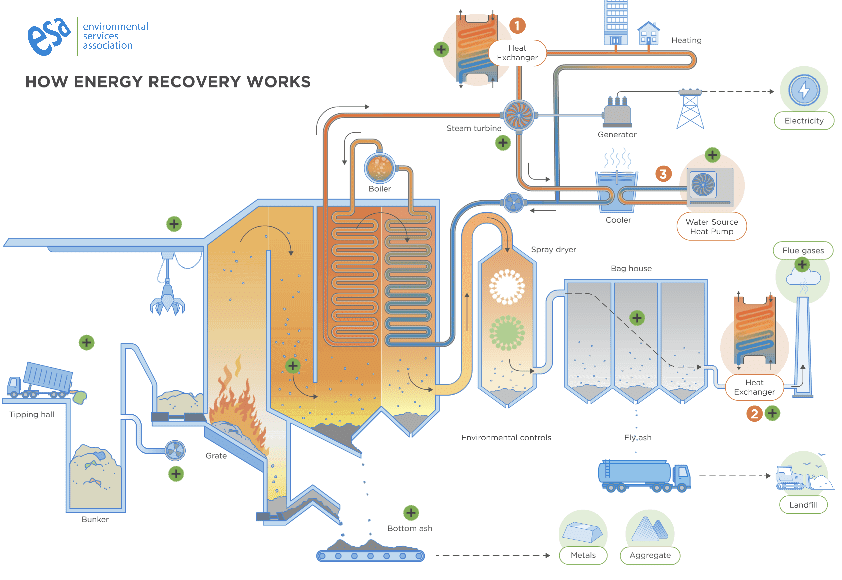
ESA members own and operate the majority of the UK’s Energy-from-Waste (EfW) fleet, which turn the rubbish left over after recycling into energy that can be supplied to electricity and heat networks.
As well as electricity and heat, metals and ash are recovered from the process to be recycled, while flue gases are carefully filtered to capture and remove pollutants so that they are not released into the atmosphere.
There are more than 60 such plants operating safely across the UK today and, combined, they produce around 4% of total UK electricity while treating around 17 million tonnes of society’s waste each year.
Treating residual waste through energy recovery has a lower greenhouse gas emissions impact than landfill, and ESA members are working to reduce emissions further through a range of measures, which include innovative Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) solutions.
You can find out more about how Energy-from-Waste works by clicking on the graphic and by reading our FAQ document.
Turning up the heat on Energy-from-Waste
Improving the energy efficiency of Energy-from-Waste (EfW) facilities by developing district heat networks could play a key role in meeting, not just our sectoral decarbonisation goals, but national net-zero targets too – since nearly a third of all UK emissions arise from heating our homes and businesses.
Heat networks operate by transporting heat produced from industrial processes, in the form of hot water or steam, through a network of insulated pipes to local communities. However, these networks are currently underutilised and serve less than three per cent of UK heat demand, unlike some Scandinavian countries which use these heat sources for more than half of their demand. In 2024, only 12 of 63 UK EfW facilities were exporting heat at scale.
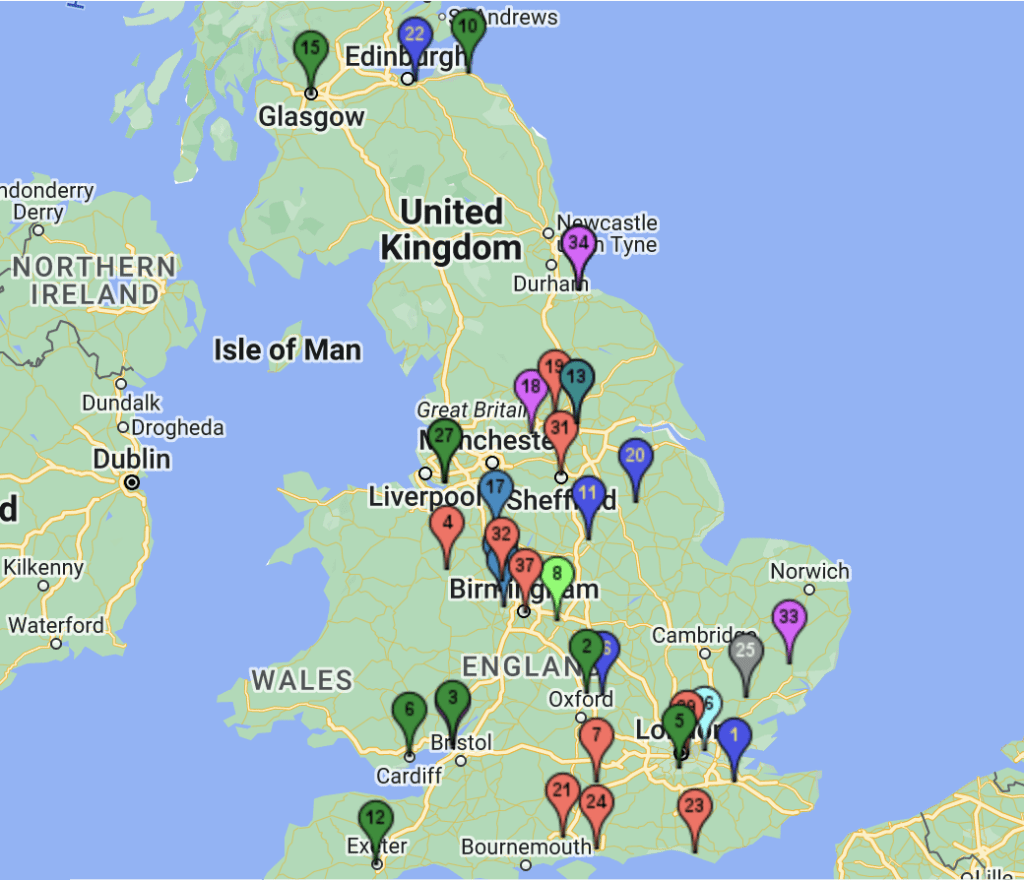
Delivering greater heat network offtake from EfW facilities will require collaboration between many different parties at scale and at pace. To support this process, the ESA has published a comprehensive Guide to Heat Offtake, and has developed an interactive Heat Network Prospectus, which provides a map of the UK’s energy- from-waste fleet along with the technical specifications and contact details for each facility.
All interested parties are welcome to view the prospectus below to support the opportunity appraisal process.
Latest decarbonising the sector news
ESA supports recommendations to bolster UK circular economy for steel scrap
The ESA has today (1st December 2025) expressed its support...
Read MoreESA guide to boost EfW heat network development
The Environmental Services Association (ESA) has published a new guide...
Read MoreThe waste sector’s journey into the Emissions Trading Scheme is heading in the right direction, but bumps in the road could remain
By Charlotte Rule, Head of Climate and Energy Policy at...
Read MoreEmissions Trading Scheme (ETS) announcement recognises role for emissions factors to ensure fair carbon-allocation and drive decarbonisation
The UK Emissions Trading Scheme (UK ETS) Authority this week...
Read More